Acetylcholine
Published: 07.05.2012
Published: 07.05.2012
You can find more information on the topic of neurotransmitters in our article by Ulrich Pontes. ▸ Neurotransmitters – Messenger Molecules in the Brain
Acetylcholin/-/acetylcholine
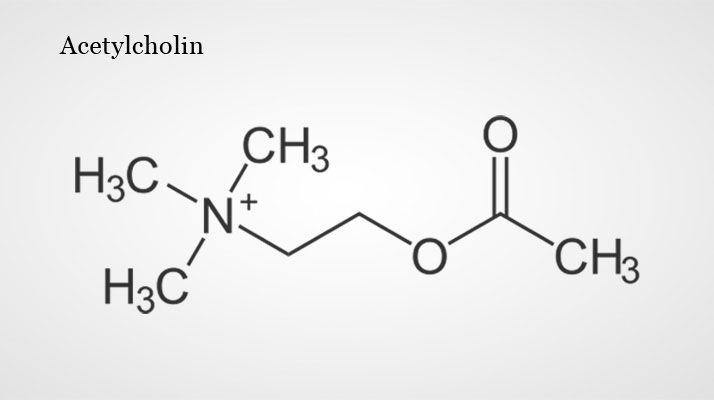
Acetylcholine is one of the most important neurotransmitters in the nervous system. In the central nervous system, it is involved in attention, learning, and memory; in the peripheral nervous system, it transmits excitation from nerves to muscles at the neuromuscular end plates and controls processes of the autonomic nervous system, i.e., the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Areas in which acetylcholine acts as a messenger substance are called cholinergic. It was the first neurotransmitter to be discovered, identified in 1921 by Otto Loewi in the heart of a frog.
Acetylcholine
Acetylcholin/-/acetylcholine
Acetylcholine is one of the most important neurotransmitters in the nervous system. In the central nervous system, it is involved in attention, learning, and memory; in the peripheral nervous system, it transmits excitation from nerves to muscles at the neuromuscular end plates and controls processes of the autonomic nervous system, i.e., the sympathetic and parasympathetic parts. Areas in which acetylcholine acts as a messenger substance are called cholinergic. It was the first neurotransmitter to be discovered, identified in 1921 by Otto Loewi in the heart of a frog.
Subjects
Author