Newly identified group of nerve cells in the brain regulates bodyweight
Obesity is a global health problem that affects many people. In recent years, very promising anti-obesity drugs have been developed. Despite these successes, there are patients who do not respond to these drugs or suffer from side effects. Therefore, there is still an unmet need for therapies. Researchers at the Max Planck Institute for Metabolism Research have now discovered a small group of nerve cells in the hypothalamus of mice brain that influence eating behavior and weight gain. This discovery could pave the way for the development of targeted anti-obesity drugs.
Veröffentlicht: 26.05.2025
- Forschende haben eine bestimmte Gruppe von Nervenzellen im Hypothalamus des Gehirns entdeckt, die das Essverhalten und die Gewichtszunahme beeinflussen.
- Diese Nervenzellen werden durch das Hormon Leptin gesteuert, das den Appetit unterdrückt.
- Entdeckung bietet Potenzial für die Entwicklung weiterer gezielter Therapien gegen Übergewicht
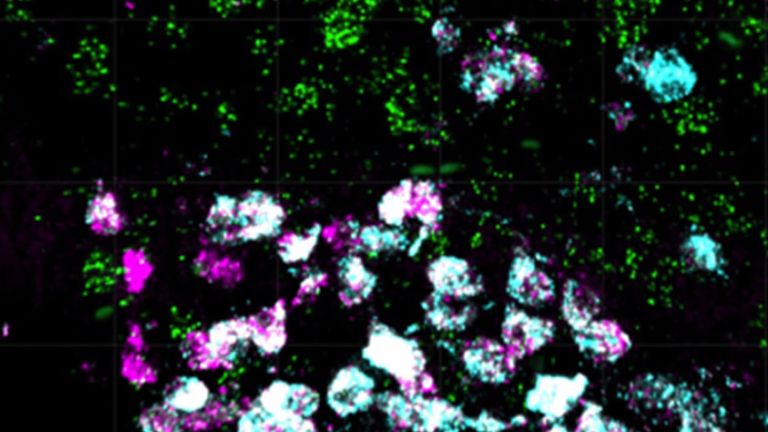
The research group identified the so-called PNOC/NPY nerve cells in the brains of mice. When activated, these cells increase food intake and lead to obesity. Interestingly, these nerve cells are also present in the human brain. Using novel genetic and molecular biological tools, the researchers were able to analyze the neurons at the single cell level and divide them into different clusters. Within this large group of nerve cells, only one cluster is responsible for the observed eating behavior.
Removing Leptin Receptors
Previous studies have shown that PNOC neurons in the hypothalamus are particularly active when mice are fed a high-fat diet. In further analyses, the researchers found that around 10% of these nerve cells have a receptor for the hormone leptin. Leptin is produced in adipose tissue and suppresses appetite in the brain. If the leptin receptor in this cluster of PNOC nerve cells was removed, the mice ate more and became overweight.
“It was surprising that such a small group of nerve cells specifically leads to obesity,” explains Marie Holm Solheim, first author of the study.
The researchers plan to continue studying these nerve cells to identify additional specific targets for potential drugs and to make them amenable to pharmacological intervention.
We hope that drugs that act on this specialized group of nerve cells will offer promising alternative therapies,” says Jens Brüning, head of the study. “However, there is still a long way to go before these can be used.”
Original publication
Marie H. Solheim, Sima Stroganov, Weiyi Chen, P. Sicilia Subagia, Corinna A. Bauder, Daria Wnuk-Lipinski, Almudena Del Río-Martín, Tamara Sotelo-Hitschfeld, Cait A. Beddows, Paul Klemm, Garron T. Dodd, Sofia Lundh, Anna Secher, F. Thomas Wunderlich, Lukas Steuernagel, Jens C. Brüning, Hypothalamic PNOC/NPY neurons constitute mediators of leptin-controlled energy homeostasis. Cell, June 2025